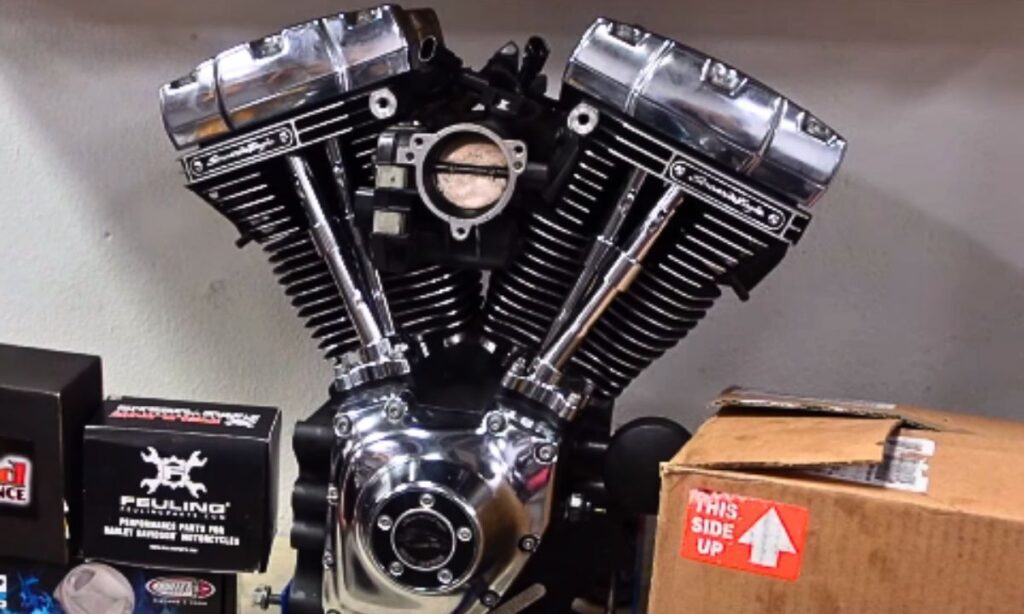
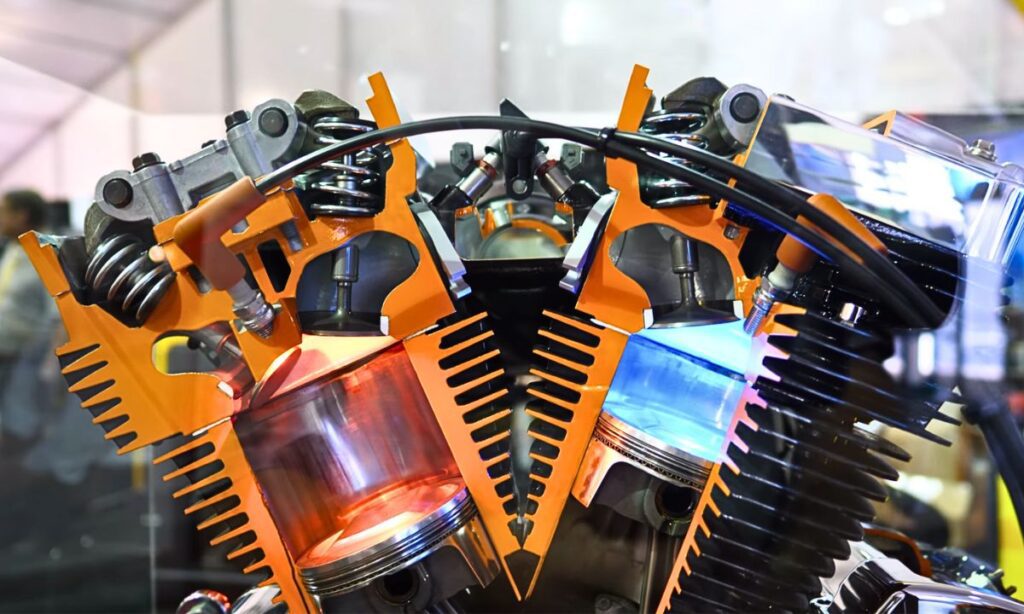
As a motorcycle enthusiast, I’ve often found myself at the centre of spirited debates around one crucial question: V-twin or Parallel Twin engines, which one truly rules the road?
In my early riding days, I was captivated by the throaty roar of a V-Twin, a sound so profound it echoed through my bones.
Yet, the smooth performance and nimbleness of a Parallel Twin also left a significant impression.
So, sit tight as we dive into the world of these two mechanical marvels, exploring their nuances, contrasts, and unique appeals to different riders.
V Twin Vs Parallel Twin
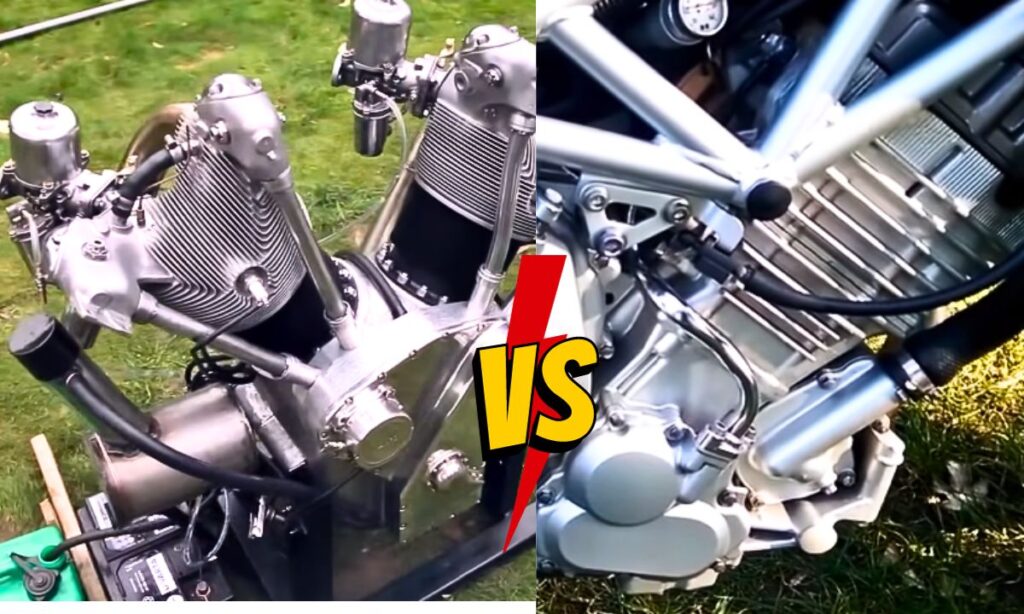
V-Twin and Parallel Twin refer to the configuration of a motorcycle’s engine.
The V-Twin engine, as the name implies, features two cylinders configured in a V shape.
This design is popular for its distinctive rumble and powerful torque at low RPMs, making it ideal for cruising and touring motorcycles.
On the other hand, the Parallel Twin engine has its two cylinders arranged side by side in a parallel configuration.
This design is praised for its smooth linear acceleration and lighter weight, making it favoured in sports and street motorcycles.
1. V-Twin Engine
V-twin engines are a popular choice for a variety of motorcycles. They’re commonly found in cruising bikes due to their distinct sound and low-end torque.
The Harley-Davidson Softail series and the Ducati Monster series are two popular models that utilize a V-Twin engine.
V-Twin engines are renowned for their distinctive sound. This sound is often described as a low rumble at idle that becomes a fierce growl at high speeds.
In terms of performance, V-Twin engines provide excellent low-end torque, making them perfect for city riding.
The power delivery is linear, which means the power increase is steady as the RPMs rise.
In a V-twin engine, the cylinders are arranged in a V-shaped configuration.
The most common angle between the two cylinders is 90 degrees, but it can vary depending on the manufacturer.
This arrangement results in a compact engine that can easily fit into a motorcycle’s frame.
2. Parallel Twin Engine
The cylinder layout and orientation in V-twin and parallel twin engines certainly contribute to their distinctive characteristics.
In a parallel twin engine, the two cylinders are positioned side by side in a vertical or inline orientation.
This configuration results in a compact engine that’s perfect for small to medium-sized motorcycles.
Parallel twin engines are common in a variety of motorcycles, from street bikes to dual-sports.
Notable examples include the Triumph Bonneville and the Kawasaki Ninja series.
Power delivery in a parallel-twin engine is typically smooth and linear, perfect if you prefer a steady, predictable response.
In terms of acoustics, each engine offers a unique sound. The parallel-twin produces a smooth and somewhat buzzy exhaust note.
3. Comparative Analysis
Comparatively, V Twin and Parallel Twin engines exhibit distinctive characteristics in terms of power, torque, vibration, cooling efficiency, and maintenance aspects.
V Twin engines typically provide high torque at low RPMs, which makes them ideal for lower-speed cruising and city riding.
On the other hand, Parallel Twin engines tend to deliver power evenly across the RPM range, making them suitable for a wide variety of riding conditions.
In terms of vibration and smoothness, V Twin engines often produce a pleasing, rhythmic vibration that many riders enjoy, but they can also be less smooth at higher speeds compared to Parallel Twin engines.
Parallel Twins, with their balanced firing order, generally offer smoother operations, particularly at higher RPMs.
V Twin engines, with their wider arrangement, allow for better airflow and cooling.
However, this design can make maintenance tasks slightly more difficult, as components are more spread out.
On the contrary, the more compact design of Parallel Twin engines can mean less efficient cooling but easier access for maintenance.
Motorcycles with V Twin engines tend to have a lower centre of gravity, which can improve handling and stability.
However, the wider engine can also lead to a wider motorcycle design.
In contrast, Parallel Twin engines allow for narrower, more compact motorcycle designs, which can be beneficial in terms of manoeuvrability and weight distribution.
Advantages and Disadvantages
V-Twin: Pros and Cons
Pros
The V-twin engine configuration is renowned for the unique characteristics that make it a favourite among motorcycle enthusiasts.
One of the primary advantages is its torque output. V-twin engines typically produce a lot of low-end torque, providing a powerful pull from a standstill.
This configuration also offers a distinct, throaty exhaust note that many bikers find appealing.
The engines are small in size, which makes the motorcycle’s design slim. Also, the V shape of the engine helps keep it cool as both engine parts are exposed to fresh air.
Cons
However, V-twin engines come with their share of drawbacks. The uneven firing order can result in more vibrations, which might lead to discomfort during long rides.
They often do not rev as high as other types of engines, which can limit top-end power.
The configuration also generally requires a heavier crankshaft to balance the engine, adding to the overall weight of the motorcycle.
Lastly, maintenance can be more challenging due to the angled arrangement of the cylinders, making some parts hard to reach.
Parallel Twin: Pros and Cons
The Parallel Twin engine configuration is a popular choice for many motorcycle enthusiasts and manufacturers.
With two cylinders arranged side by side in a parallel alignment, this engine type offers several advantages.
Pros
Parallel twin engines generally provide smoother operation due to better primary balance, resulting in less vibration at high speeds.
The parallel construction makes it simpler to work on the engine, which can be a significant advantage for self-maintenance.
These engines are typically cheaper to manufacture and maintain, making bikes with parallel twin engines more affordable for consumers.
The parallel twin’s compact and lightweight design makes it ideal for smaller, agile motorcycles.
This compactness aids in multiple aspects, including better fuel economy and easier handling.
Cons
While parallel twin engines are known for their smooth operation, they might not deliver the same power output as other configurations like the V-Twin.
Despite the smoother operation at higher speeds, parallel twins can exhibit increased vibration at lower RPMs.
Some riders find the exhaust note of a parallel twin engine less appealing than the deeper, throatier sound of a V-Twin.
Which One Is Best V Twin Vs Parallel Twin?
When it comes to the question of which one is better, a V-Twin or a Parallel Twin engine, the answer largely depends on your specific needs and preferences.
V-twin engines, named for their formation where two cylinders form a V shape, are known for their strong low-end torque and unique “rumbling” sound.
On the other hand, Parallel Twin engines, where the two cylinders are positioned side by side, are typically found in sports and off-road bikes.
Both twin engines have their own unique advantages. If you prefer low-end torque, an iconic sound, and a laid-back ride, the V-Twin might be your best choice.
However, if you’re after high RPM performance, fuel efficiency, and smoothness, you might find the Parallel Twin more to your liking.


Talha Younas, the brains behind the influential motorcycle-focused website, TwoWheller.com, is a dedicated and passionate advocate for biking culture. Born and raised in a family of motorcycle enthusiasts, his love for two-wheeled transportation was ignited at an early age. His commitment to providing in-depth reviews and helpful tips for riders has established him as a respected figure in the motorcycle community.

